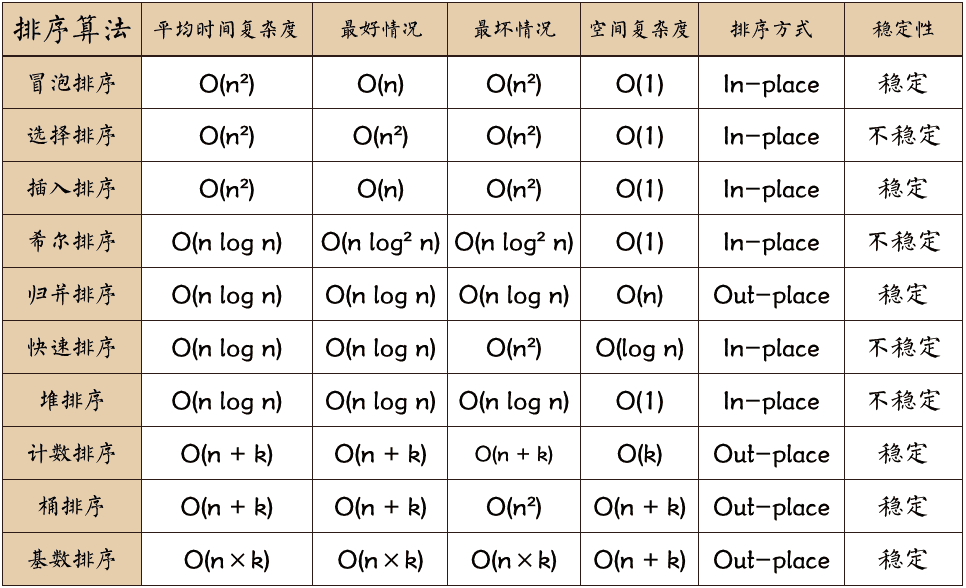
面试算法准备(Java) 十大经典排序算法 经典的十大排序算法可以大致分为两类:
比较类排序:
冒泡排序 =》快速排序(冒泡排序优化)
插入排序=》希尔排序(插入排序优化)
选择排序=》堆排序(选择排序优化)
归并排序(二路、多路)
非比较类排序:
稳定排序和非稳定排序是根据排序后相等元素的相对位置来区分的
稳定排序和不稳定排序 - 紫红的泪 - 博客园
冒泡排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 public class BubbleSort { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] ints = new int []{2343 , 234 , 765 , 1 , 23 , 5 , 3 , 2 , 0 , 3 }; bubbleSort(ints); for (int i : ints) { System.out.print(i + "\t" ); } } public static void bubbleSort (int [] ints) { for (int i = 0 ; i < ints.length - 1 ; i++) { boolean isChange = false ; for (int j = 0 ; j < ints.length - 1 - i; j++) { if (ints[j] > ints[j + 1 ]) { int swap = ints[j]; ints[j] = ints[j + 1 ]; ints[j + 1 ] = swap; isChange = true ; } } if (!isChange) { break ; } } } }
快速排序 碰巧每次基准值都是极值,划分下次划分Tn-1,整体就是On^2了
《啊哈!算法》 关于快速排序法为什么一定要哨兵j 先出动的原因?_快速排序先移动j-CSDN博客
用下面代码,结合例子1 2 3 4,就知道为什么right先动了,不然不对
用7 7 6 3 8 12,就能想明白为什么不是稳定的了,两个7的先后顺序不对了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 public class QuickSort { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] ints = new int []{2343 , 234 , 765 , 1 , 23 , 5 , 3 , 2 , 0 , 3 }; quickSort(ints, 0 , ints.length - 1 ); for (int i : ints) { System.out.print(i + "\t" ); } } public static void quickSort (int [] ints, int left, int right) { if (left >= right) { return ; } int start = left; int end = right; while (start < end) { while (start < end && ints[end] >= ints[left]) { end--; } while (start < end && ints[start] <= ints[left]) { start++; } if (start == end) { int temp = ints[left]; ints[left] = ints[end]; ints[end] = temp; } else { int temp = ints[start]; ints[start] = ints[end]; ints[end] = temp; } } quickSort(ints, left, start - 1 ); quickSort(ints, start + 1 , right); } }
插入排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 public class InsertionSort { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] ints = new int []{2343 , 234 , 765 , 1 , 23 , 5 , 3 , 2 , 0 , 3 }; insertionSort(ints); for (int i : ints) { System.out.print(i + "\t" ); } } public static void insertionSort (int [] ints) { for (int i = 1 ; i < ints.length; i++) { int index = i; int value = ints[i]; for (int j = i - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) { if (ints[j] > value) { ints[j + 1 ] = ints[j]; } else { ints[j + 1 ] = value; break ; } if (j == 0 ) { ints[j] = value; } } while (index > 0 && ints[index - 1 ] > value) { ints[index] = ints[index - 1 ]; index--; } ints[index] = value; } } }
希尔排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 public class ShellSort { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] ints = new int []{2343 , 234 , 765 , 1 , 23 , 5 , 3 , 2 , 0 , 3 }; shellSort(ints); for (int i : ints) { System.out.print(i + "\t" ); } } public static void shellSort (int [] ints) { for (int i = ints.length / 2 ; i > 0 ; i /= 2 ) { for (int j = i; j < ints.length; j++) { int index = j; int value = ints[j]; while (index - i >= 0 && ints[index - i] > value) { ints[index] = ints[index - i]; index -= i; } ints[index] = value; } } } }
选择排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 public class SelectSort { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] ints = new int []{2343 , 234 , 765 , 1 , 23 , 5 , 3 , 2 , 0 , 3 }; selectSort(ints); for (int i : ints) { System.out.print(i + "\t" ); } } public static void selectSort (int [] ints) { for (int i = ints.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { int max_index = i; for (int j = i - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) { if (ints[j] > ints[max_index]) { max_index = j; } } if (max_index != i) { int temp = ints[i]; ints[i] = ints[max_index]; ints[max_index] = temp; } } } }
堆排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 public class HeapSort { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] ints = new int []{2343 , 234 , 765 , 1 , 23 , 5 , 3 , 2 , 0 , 3 }; heapSort(ints); for (int i : ints) { System.out.print(i + "\t" ); } } public static void heapSort (int [] ints) { for (int i = ints.length / 2 - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { heapSortStart(ints, ints.length, i); } for (int i = ints.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { swap(ints, i, 0 ); heapSortStart(ints, i, 0 ); } } public static void heapSortStart (int [] ints, int length, int i) { int largest = i; int lson = i * 2 + 1 , rson = i * 2 + 2 ; if (lson < length && ints[lson] > ints[largest]) { largest = lson; } if (rson < length && ints[rson] > ints[largest]) { largest = rson; } if (largest != i) { swap(ints, largest, i); heapSortStart(ints, length, largest); } } public static void swap (int [] ints, int left, int right) { int temp = ints[left]; ints[left] = ints[right]; ints[right] = temp; } }
归并排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 public class MergeSort { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] ints = new int []{2343 , 234 , 765 , 1 , 23 , 5 , 3 , 2 , 0 , 3 }; mergeSort(ints, 0 , ints.length - 1 ); for (int i : ints) { System.out.print(i + "\t" ); } } public static void mergeSort (int [] ints, int left, int right) { if (left < right) { int mid = (left + right) / 2 ; mergeSort(ints, left, mid); mergeSort(ints, mid + 1 , right); merge(ints, left, mid, right, new int [ints.length]); } } public static void merge (int [] ints, int left, int mid, int right, int [] temp) { int left_start = left; int right_start = mid + 1 ; int index = 0 ; while (left_start <= mid && right_start <= right) { if (ints[left_start] <= ints[right_start]) { temp[index++] = ints[left_start++]; } else { temp[index++] = ints[right_start++]; } } while (left_start <= mid) { temp[index++] = ints[left_start++]; } while (right_start <= right) { temp[index++] = ints[right_start++]; } for (int i = 0 ; i < index; i++) { ints[left++] = temp[i]; } } }
计数排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 public class CountingSort { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] ints = new int []{2343 , 234 , 765 , 1 , 23 , 5 , 3 , 2 , 0 , 3 }; countingSort(ints); for (int i : ints) { System.out.print(i + "\t" ); } } public static void countingSort (int [] ints) { if (ints == null || ints.length == 0 ) { return ; } int max = ints[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < ints.length; i++) { if (ints[i] > max) { max = ints[i]; } } int [] temp = new int [max + 1 ]; for (int i : ints) { temp[i]++; } int t = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < temp.length; i++) { if (temp[i] != 0 ) { for (int j = 0 ; j < temp[i]; j++) { ints[t++] = i; } } } } }
桶排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 public class BucketSort { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] ints = new int []{2343 , 234 , 765 , 1 , 23 , 5 , 3 , 2 , 0 , 3 }; bucketSort(ints); for (int i : ints) { System.out.print(i + "\t" ); } } public static void bucketSort (int [] ints) { if (ints == null || ints.length == 1 ) { return ; } int min = ints[0 ]; int max = ints[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < ints.length; i++) { if (ints[i] > max) { max = ints[i]; } if (ints[i] < min) { min = ints[i]; } } int buketNum = (max - min) / ints.length + 1 ; ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> bucketList = new ArrayList <>(buketNum); for (int i = 0 ; i < buketNum; i++) { bucketList.add(new ArrayList <>()); } for (int i : ints) { bucketList.get((i - min) / ints.length).add(i); } for (int i = 0 ; i < buketNum; i++) { Collections.sort(bucketList.get(i)); } int t = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < buketNum; i++) { ArrayList<Integer> list = bucketList.get(i); for (Integer integer : list) { ints[t++] = integer; } } } }
基数排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 public class RadixSort { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] ints = new int []{2343 , 234 , 765 , 1 , 23 , 5 , 3 , 2 , 0 , 3 }; radixSort(ints); for (int i : ints) { System.out.print(i + "\t" ); } } public static void radixSort (int [] ints) { if (ints == null || ints.length == 1 ) { return ; } int [][] save = new int [10 ][ints.length]; int [] bucket_num = new int [10 ]; int max = ints[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < ints.length; i++) { if (ints[i] > max) { max = ints.length; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < (max + "" ).length(); i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < ints.length; j++) { int temp = ints[j] / (int ) Math.pow(10 , i) % 10 ; save[temp][bucket_num[temp]++] = ints[j]; } int t = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < bucket_num.length; j++) { if (bucket_num[j] != 0 ) { for (int k = 0 ; k < bucket_num[j]; k++) { ints[t++] = save[j][k]; } } bucket_num[j] = 0 ; } } } }
题目练手链接
LCR 159. 库存管理 III - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 class Solution { public int [] inventoryManagement(int [] stock, int cnt) { int [] temp = new int [stock.length]; heapSort(stock); int [] result = new int [cnt]; for (int i = 0 ; i < cnt; i++) { result[i] = stock[i]; } return result; } public void mergeSort (int [] stock, int [] temp, int start, int end) { if (start < end) { int mid = start + (end - start) / 2 ; mergeSort(stock, temp, start, mid); mergeSort(stock, temp, mid + 1 , end); merge(stock, temp, start, mid, end); } } public void merge (int [] stock, int [] temp, int start, int mid, int end) { int left = start, right = mid + 1 , t = start; while (left <= mid && right <= end) { if (stock[left] <= stock[right]) { temp[t++] = stock[left++]; } else { temp[t++] = stock[right++]; } } while (left <= mid) { temp[t++] = stock[left++]; } while (right <= end) { temp[t++] = stock[right++]; } for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) { stock[i] = temp[i]; } } public void bubbleSort (int [] stock) { boolean flag = true ; for (int i = 1 ; i < stock.length; i++) { if (flag) { boolean temp = false ; for (int j = 1 ; j <= stock.length - i; j++) { if (stock[j - 1 ] > stock[j]) { temp = true ; int change = stock[j - 1 ]; stock[j - 1 ] = stock[j]; stock[j] = change; } } flag = temp; } } } public void selectSort (int [] stock) { for (int i = 1 ; i < stock.length; i++) { int max = 0 ; for (int j = 1 ; j <= stock.length - i; j++) { if (stock[j] > stock[max]) { max = j; } } int temp = stock[max]; stock[max] = stock[stock.length - i]; stock[stock.length - i] = temp; } } public void quickSort (int [] stock, int start, int end) { if (start >= end) { return ; } int left = start, right = end; while (left < right) { while (left < right && stock[right] >= stock[start]) { right--; } while (left < right && stock[left] <= stock[start]) { left++; } if (left < right) { int temp = stock[left]; stock[left] = stock[right]; stock[right] = temp; } } int temp = stock[start]; stock[start] = stock[left]; stock[left] = temp; quickSort(stock, start, left); quickSort(stock, left + 1 , end); } public void heapSort (int [] stock) { for (int i = stock.length / 2 - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { heapify(stock, stock.length, i); } for (int i = stock.length - 1 ; i > 0 ; i--) { int temp = stock[0 ]; stock[0 ] = stock[i]; stock[i] = temp; heapify(stock, i, 0 ); } } public void heapify (int [] stock, int n, int i) { int largest = i, left = 2 * i + 1 , right = 2 * i + 2 ; if (left < n && stock[left] > stock[largest]) { largest = left; } if (right < n && stock[right] > stock[largest]) { largest = right; } if (largest != i) { int temp = stock[largest]; stock[largest] = stock[i]; stock[i] = temp; heapify(stock, n, largest); } } }
牛客网面试必刷Top101 链表
BM1 反转链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public ListNode ReverseList (ListNode head) { ListNode lastNode = null ; while (head != null ) { ListNode temp = head.next; head.next = lastNode; lastNode = head; head = temp; } return lastNode; } }
BM2 链表内指定区间反转
懵逼,细看
时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(1),一次遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public ListNode reverseBetween (ListNode head, int m, int n) { ListNode start = new ListNode (-1 ); start.next = head; ListNode last = start; ListNode cur = head; for (int i = 1 ; i < m; i++) { last = cur; cur = cur.next; } for (int i = m; i < n; i++) { ListNode temp = cur.next; cur.next = temp.next; temp.next = last.next; last.next = temp; } return start.next; } }
BM4 合并两个排序的链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public ListNode Merge (ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) { ListNode result = null ,first = pHead1,second = pHead2,tmp = null ,last = null ; while (first!=null &&second!=null ){ if (first.val<second.val){ tmp = first; first = first.next; }else { tmp = second; second = second.next; } ListNode newNode = new ListNode (tmp.val); if (result==null ){ result = newNode; last = result; }else { last.next = newNode; last = last.next; } } while (first!=null ){ ListNode newNode = new ListNode (first.val); if (result==null ){ result = newNode; last = result; }else { last.next = newNode; last = last.next; } first = first.next; } while (second!=null ){ ListNode newNode = new ListNode (second.val); if (result==null ){ result = newNode; last = result; }else { last.next = newNode; last = last.next; } second = second.next; } return result; } }
递归实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class Solution { public ListNode Merge (ListNode list1,ListNode list2) { if (list1==null ){ return list2; } else if (list2==null ){ return list1; } if (list2.val>list1.val){ list1.next = Merge(list1.next,list2); return list1; } else { list2.next = Merge(list1,list2.next); return list2; } } }
BM5 合并k个已排序的链表
时间复杂度要为O(nlogn)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 ``` <a id="BM6 判断链表中是否有环" ></a> **BM6 判断链表中是否有环** 快慢指针,如果有环会碰到一起 ```java import java.util.*;public class Solution { public boolean hasCycle (ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (fast == slow) { return true ; } } return false ; } }
BM7 链表中环的入口结点
空间复杂度 O(1),时间复杂度 O(n)
据题干,不说别的,我们能发现这道题需要完成两个任务:
判断链表是否有环。(这个前面有)
在有环的链表中找到环的入口。
具体做法:(证明不看了,从链表头经过环入口到达相遇地方经过的距离等于整数倍环的大小,那我们从头开始遍历到相遇位置,和从相遇位置开始在环中遍历,会使用相同的步数,而双方最后都会经过入口到相遇位置这y个节点)
step 1:使用BM6.判断链表中是否有环中的方法判断链表是否有环,并找到相遇的节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop (ListNode pHead) { ListNode fast = pHead, slow = pHead, slow_real = null ; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (fast == slow) { slow_real = slow; break ; } } if (slow_real == null ) { return null ; } fast = pHead; while (fast != slow_real) { fast = fast.next; slow_real = slow_real.next; } return slow_real; } }
BM8 链表中倒数最后k个结点
最简单的思路就是借助栈,但是空间复杂度为O(n)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public ListNode FindKthToTail (ListNode pHead, int k) { List<ListNode>list = new ArrayList <>(); ListNode tmp = pHead; while (tmp!=null ){ list.add(tmp); tmp = tmp.next; } if (list.size()<k||k==0 ){ return null ; }else { return list.get(list.size()-k); } } }
还有简单的思路就是先遍历一遍到最后,这样就知道链表的长度,这样就可以再遍历一次看遍历多少个节点就找到正确的节点了
进阶思路为空间复杂度为O(1),快慢指针,学习这种思路
(双指针指的是在遍历对象的过程中,不是普通的使用单个指针进行访问,而是使用两个指针(特殊情况甚至可以多个),两个指针或是同方向访问两个链表、或是同方向访问一个链表(快慢指针)、或是相反方向扫描(对撞指针),从而达到我们需要的目的。)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public ListNode FindKthToTail (ListNode pHead, int k) { ListNode slow = pHead; ListNode fast = pHead; for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) { if (fast != null ) { fast = fast.next; } else { return null ; } } while (fast != null ) { fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } return slow; } }
BM10 两个链表的第一个公共结点
要求空间复杂度为O(1)
使用两个指针N1,N2,一个从链表1的头节点开始遍历,我们记为N1,一个从链表2的头节点开始遍历,我们记为N2。
让N1和N2一起遍历,当N1先走完链表1的尽头(为null)的时候,则从链表2的头节点继续遍历,同样,如果N2先走完了链表2的尽头,则从链表1的头节点继续遍历,也就是说,N1和N2都会遍历链表1和链表2。
因为两个指针,同样的速度,走完同样长度(链表1+链表2),不管两条链表有无相同节点,都能够到达同时到达终点。
(N1最后肯定能到达链表2的终点,N2肯定能到达链表1的终点)。
所以,如何得到公共节点:
有公共节点的时候,N1和N2必会相遇,因为长度一样嘛,速度也一定,必会走到相同的地方的,所以当两者相等的时候,则会第一个公共的节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode (ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) { ListNode t1 = pHead1, t2 = pHead2; while (t1 != t2) { t1 = (t1 == null ) ? pHead2 : t1.next; t2 = (t2 == null ) ? pHead1 : t2.next; } return t1; } }
BM11 链表相加(二)
step 1:任意一个链表为空,返回另一个链表就行了,因为链表为空相当于0,0加任何数为0,包括另一个加数为0的情况。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public ListNode addInList (ListNode head1, ListNode head2) { if (head1==null ){ return head2; } if (head2==null ){ return head1; } head1 = reverseList(head1); head2 = reverseList(head2); ListNode start = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode head = start; int carry = 0 ; while (head1 != null || head2 != null || carry != 0 ) { int val1, val2; if (head1 == null ) { val1 = 0 ; } else { val1 = head1.val; } if (head2 == null ) { val2 = 0 ; } else { val2 = head2.val; } head.next = new ListNode ((val1 + val2 + carry) % 10 ); head = head.next; carry = (val1 + val2 + carry) / 10 ; if (head1 != null ) { head1 = head1.next; } if (head2 != null ) { head2 = head2.next; } } return reverseList(start.next); } public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { if (head == null ) { return null ; } ListNode cur = head; ListNode last = null ; while (cur != null ) { ListNode temp = cur.next; cur.next = last; last = cur; cur = temp; } return last; } }
BM12 单链表的排序
简单的思路就是遍历单链表转换成数组进行排序,这里学基于链表的归并排序
step 1:首先判断链表为空或者只有一个元素,直接就是有序的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public ListNode sortInList (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ) { return head; } ListNode left = head, mid = head.next, right = head.next.next; while (right != null && right.next != null ) { left = left.next; mid = mid.next; right = right.next.next; } left.next = null ; return merge(sortInList(head), sortInList(mid)); } public ListNode merge (ListNode head1, ListNode head2) { if (head1 == null ) { return head2; } if (head2 == null ) { return head1; } ListNode start = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode cur = start; while (head1 != null && head2 != null ) { if (head1.val <= head2.val) { cur.next = head1; head1 = head1.next; } else { cur.next = head2; head2 = head2.next; } cur = cur.next; } if (head1 != null ) { cur.next = head1; } if (head2 != null ) { cur.next = head2; } return start.next; } }
BM13 判断一个链表是否为回文结构
借助List实现很容易,就先遍历链表然后将链表的所有值都放到List中,然后双指针对碰即可,如果在碰撞之前某个值不一样就返回fasle即可
学习双指针找中点的方法,空间复杂度为O(1),快慢指针
我们首先来看看中点的特征,一个链表的中点,距离链表开头是一半的长度,距离链表结尾也是一半的长度,那如果从链表首遍历到链表中点位置,另一个每次遍历两个节点的指针是不是就到了链表尾,那这时候我们的快慢双指针就登场了:
具体做法:
step 1:慢指针每次走一个节点,快指针每次走两个节点,快指针到达链表尾的时候,慢指针刚好到了链表中点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public boolean isPail (ListNode head) { if (head == null ) { return true ; } ListNode slow = head, fast = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; } ListNode start = slow, last = null ; while (start != null ) { ListNode tmp = start.next; start.next = last; last = start; start = tmp; } slow = last; fast = head; while (slow != null ) { if (slow.val != fast.val) { return false ; } slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } return true ; } }
BM14 链表的奇偶重排
空间复杂度O(1),时间复杂度O(n)
step 1:判断空链表的情况,如果链表为空,不用重排。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public ListNode oddEvenList (ListNode head) { if (head == null ) { return head; } ListNode even = head.next, odd = head; ListNode start = even; while (even != null && even.next != null ) { odd.next = even.next; odd = odd.next; even.next = odd.next; even = even.next; } odd.next = start; return head; } }
BM15 删除有序链表中重复的元素-I
要求空间复杂度为O(1)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) { if (head == null ) { return null ; } ListNode last = head, result = head; while (head.next != null ) { head = head.next; if (last.val == head.val) { last.next = null ; } else { last.next = head; last = head; } } return result; } }
BM16 删除有序链表中重复的元素-II
进阶要求空间复杂度为O(1)
step 1:给链表前加上表头,方便可能的话删除第一个节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) { if (head == null ) { return null ; } ListNode node = new ListNode (0 ); node.next = head; ListNode cur = node; while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null ) { if (cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val) { int temp = cur.next.val; while (cur.next != null && cur.next.val == temp) { cur.next = cur.next.next; } }else { cur = cur.next; } } return node.next; } }
二分查找
BM17 二分查找-I
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int search (int [] nums, int target) { int result = -1 ; int left = 0 , right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left <= right) { int mid = (left + right) / 2 ; if (nums[mid] == target) { result = mid; break ; } else if (nums[mid] > target) { right = mid - 1 ; } else { left = mid + 1 ; } } return result; } }
BM19 寻找峰值
直接去寻找最大值,那么最大值一定就是峰值,这个简单,这里学习使用二分法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int findPeakElement (int [] nums) { int left = 0 , right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left < right) { int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ; if (nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1 ]) { right = mid; } else { left = mid + 1 ; } } return left; } }
BM20 数组中的逆序对
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int InversePairs (int [] nums) { int [] temp = new int [nums.length]; return mergeSort(nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 , temp); } public int mergeSort (int [] nums, int left, int right, int [] temp) { if (left >= right) { return 0 ; } int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ; int result = mergeSort(nums, left, mid, temp) + mergeSort(nums, mid + 1 , right, temp); result %= 1000000007 ; int l = left, r = mid + 1 , t = left; while (l <= mid && r <= right) { if (nums[l] > nums[r]) { result += mid - l + 1 ; temp[t++] = nums[r++]; } else { temp[t++] = nums[l++]; } } while (l <= mid) { temp[t++] = nums[l++]; } while (r <= right) { temp[t++] = nums[r++]; } for (t = left; t <= right; t++) { nums[t] = temp[t]; } return result % 1000000007 ; } }
BM21 旋转数组的最小数字
最简单方法就是维护最小值以O(n)的时间复杂度去找最小值呗,看下面二分法,也有双指针思想
step 1:双指针指向旋转后数组的首尾,作为区间端点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int minNumberInRotateArray (int [] nums) { if (nums.length==0 ){ return 0 ; } int left = 0 ,right = nums.length -1 ; while (left<right){ int mid = (left+right)/2 ; if (nums[mid]>nums[right]) left = mid+1 ; else if (nums[mid]<nums[right]) right = mid; else right--; } return nums[left]; } }
BM22 比较版本号
直接spilt转字符串数组,之后较短的数组不能取到内容就是为0,然后将当前需要判断的值转数字(这里易错的就是”0.226”,”0.38”比较那么0.38更大)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int compare (String version1, String version2) { String[] nums1 = version1.split("\\." ); String[] nums2 = version2.split("\\." ); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums1.length || i < nums2.length; i++){ String str1 = i < nums1.length ? nums1[i] : "0" ; String str2 = i < nums2.length ? nums2[i] : "0" ; long num1 = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < str1.length(); j++) num1 = num1 * 10 + (str1.charAt(j) - '0' ); long num2 = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < str2.length(); j++) num2 = num2 * 10 + (str2.charAt(j) - '0' ); if (num1 > num2) return 1 ; if (num1 < num2) return -1 ; } return 0 ; } }
学下面的方法,主要就是转换为数字的思想
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int compare (String version1, String version2) { int i = 0 , j = 0 ; while (i < version1.length() | j < version2.length()) { long num1 = 0 ; while (i < version1.length() && version1.charAt(i) != '.' ) { num1 = num1 * 10 + (version1.charAt(i) - '0' ); i++; } i++; long num2 = 0 ; while (j < version2.length() && version2.charAt(j) != '.' ) { num2 = num2 * 10 + (version2.charAt(j) - '0' ); j++; } j++; if (num1 > num2) { return 1 ; } else if (num1 < num2) { return -1 ; } } return 0 ; } }
二叉树
BM23 二叉树的前序遍历
递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 import java.util.*;public class Solution { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); public int [] preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer>tmp = pre(root); int [] ints = new int [tmp.size()]; int i = 0 ; for (int ii : tmp) { ints[i++] = ii; } return ints; } List<Integer> pre (TreeNode node) { if (node == null ) { return list; } list.add(node.val); pre(node.left); pre(node.right); return list; } }
迭代
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int [] preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return new int [0 ]; } ArrayList<Integer>list = new ArrayList <>(); Stack<TreeNode>stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode temp = stack.pop(); list.add(temp.val); if (temp.right != null ) { stack.push(temp.right); } if (temp.left != null ) { stack.push(temp.left); } } int [] ints = new int [list.size()]; for (int i = 0 ; i < list.size(); i++) { ints[i] = list.get(i); } return ints; } }
BM25 二叉树的后序遍历
递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 import java.util.*;public class Solution { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); public int [] postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer>tmp = last(root); int [] ints = new int [tmp.size()]; int i = 0 ; for (int ii : tmp) { ints[i++] = ii; } return ints; } List<Integer> last (TreeNode node) { if (node == null ) { return list; } last(node.left); last(node.right); list.add(node.val); return list; } }
堆/栈/队列
BM42 用两个栈实现队列
插入直接插入stack1,需要读取的时候需要看stack2有没有内容,没有就需要将stack1的值放到stack2中,这样stack2的顶就是队列的头,也就是stack1保存新插入的值倒序,stack2保存正序的值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import java.util.*;import java.util.Stack;public class Solution { Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack <Integer>(); Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack <Integer>(); public void push (int node) { stack1.push(node); } public int pop () { if (stack2.size()<=0 ){ while (stack1.size()!=0 ){ stack2.push(stack1.pop()); } } return stack2.pop(); } }
BM43 包含min函数的栈
BM44 有效括号序列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public boolean isValid (String s) { Stack<Character> stack = new Stack <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { char c = s.charAt(i); if (c == '(' || c == '[' || c == '{' ) { stack.push(c); } else { if (stack.isEmpty()){ return false ; } char tmp = stack.pop(); if (!((tmp == '(' && c == ')' ) || (tmp == '[' && c == ']' ) || (tmp == '{' && c == '}' ))) { return false ; } } } if (!stack.isEmpty()) { return false ; } return true ; } }
BM46 最小的K个数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 ``` ### 哈希 - <a href = "#BM51 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字" >**BM51 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字**</a> - <a href="BM52 数组中只出现一次的两个数字" >**BM52 数组中只出现一次的两个数字**</a> - <a href= "#BM53 缺失的第一个正整数" >**BM53 缺失的第一个正整数**</a> <a id="BM51 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字" ></a> **BM51 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字** 其实不用哈希,摩尔投票即可 ```java import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution (int [] numbers) { int result = numbers[0 ], power = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < numbers.length; i++) { if (numbers[i] != result) { power--; } else { power++; } if (power == 0 ) { result = numbers[i]; power = 1 ; } } return result; } }
BM52 数组中只出现一次的两个数字
借助哈希表的方式很简单,哈希表中存在这个键就移除,不存在就往里面放,这样只出现一次的键最后一定会存在于哈希表中,出现两次的就会再加入后被移除掉了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int [] FindNumsAppearOnce (int [] nums) { HashMap<Integer, Object>map = new HashMap <Integer, Object>(); for (int i : nums) { if (map.containsKey(i)) { map.remove(i, null ); } else { map.put(i, null ); } } int [] result = new int [2 ]; int t = 0 ; for (Integer i : map.keySet()) { result[t++] = i; } return result; } }
BM53 缺失的第一个正整数
空间为O(n)的方法,借助哈希表往里面插值,按照正整数从小到大查看hashmap中是否存在在哈希表中,找到最小的不在哈希表中返回即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int minNumberDisappeared (int [] nums) { int length = nums.length; HashMap<Integer, Integer>map = new HashMap <Integer, Integer>(); for (int i : nums) { map.put(i, 1 ); } int result = 1 ; while (map.containsKey(result)) { result++; } return result; } }
哈希表是一种根据关键码(key)直接访问值(value)的一种数据结构。而这种直接访问意味着只要知道key就能在O(1)时间内得到value,因此哈希表常用来统计频率、快速检验某个元素是否出现过等。
进阶(学这种),原地哈希,时间复杂度为O(n),多次遍历数组,都是单层循环;空间复杂度为O(1),原地哈希,以索引为指向,没有额外空间
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 ``` ### 递归/回溯 全排列问题,找出所有可能的问题,从所有可能找出一种可能,需要重复回溯的问题,答案为树状要恢复状态和线性无需恢复状态。重点就是找到满足题目要求的排除条件和递归规则条件 - **<a href="#BM55 没有重复项数字的全排列" >BM55 没有重复项数字的全排列</a>** - **<a href="#BM56 有重复项数字的全排列" >BM56 有重复项数字的全排列</a>** - **<a href="#BM57 岛屿数量" >BM57 岛屿数量</a>** - **<a href="#BM58 字符串的排列" >BM58 字符串的排列</a>** - **<a href="#BM60 括号生成" >BM60 括号生成</a>** - **<a href="#BM61 矩阵最长递增路径" >BM61 矩阵最长递增路径</a>** <a name="BM55 没有重复项数字的全排列" ></a> **BM55 没有重复项数字的全排列** 递归是一个过程或函数在其定义或说明中有直接或间接调用自身的一种方法,它通常把一个大型复杂的问题层层转化为一个与原问题相似的规模较小的问题来求解。因此递归过程,最重要的就是查看能不能讲原本的问题分解为更小的子问题,这是使用递归的关键。 如果是线型递归,子问题直接回到父问题不需要回溯,但是如果是树型递归,父问题有很多分支,我需要从子问题回到父问题,进入另一个子问题。因此回溯是指在递归过程中,从某一分支的子问题回到父问题进入父问题的另一子问题分支,因为有时候进入第一个子问题的时候修改过一些变量,因此回溯的时候会要求改回父问题时的样子才能进入第二子问题分支。 **思路:** 全排列就是对数组元素交换位置,使每一种排列都可能出现。因为题目要求按照字典序排列输出,那毫无疑问第一个排列就是数组的升序排列,它的字典序最小,后续每个元素与它后面的元素交换一次位置就是一种排列情况,但是如果要保持原来的位置不变,那就不应该从它后面的元素开始交换而是从自己开始交换才能保证原来的位置不变,不会漏情况。 如何保证每个元素能和从自己开始后的每个元素都交换位置,这种时候我们可以考虑递归。为什么可以使用递归?我们可以看数组[1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ],如果遍历经过一个元素2 以后,那就相当于我们确定了数组到该元素为止的前半部分,前半部分1 和2 的位置都不用变了,只需要对3 ,4 进行排列,这对于后半部分而言同样是一个全排列,同样要对从每个元素开始往后交换位置,因此后面部分就是一个**子问题**。那我们考虑递归的几个条件: - **终止条件:** 要交换位置的下标到了数组末尾,没有可交换的了,那这就构成了一个排列情况,可以加入输出数组。 - **返回值:** 每一级的子问题应该把什么东西传递给父问题呢,这个题中我们是交换数组元素位置,前面已经确定好位置的元素就是我们返还给父问题的结果,后续递归下去会逐渐把整个数组位置都确定,形成一种排列情况。 - **本级任务:** 每一级需要做的就是遍历从它开始的后续元素,每一级就与它交换一次位置。 如果只是使用递归,我们会发现,上例中的1 与3 交换位置以后,如果2 再与4 交换位置的时候,我们只能得到3412 这种排列,无法得到1432 这种情况。这是因为遍历的时候1 与3 交换位置在2 与4 交换位置前面,递归过程中就默认将后者看成了前者的子问题,但是其实我们1 与3 没有交换位置的情况都没有结束,相当于上述图示中只进行了第一个分支。因此我们用到了**回溯**。处理完1 与3 交换位置的子问题以后,我们再将其交换回原来的情况,相当于上述图示回到了父节点,那后续完整的情况交换我们也能得到。 ```java import java.util.*;public class Solution { public void swap (ArrayList<Integer> list, int i1, int i2) { int temp = list.get(i1); list.set(i1, list.get(i2)); list.set(i2, temp); } public void backTrack (ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>result, ArrayList<Integer>num, int index) { if (index == num.size() - 1 ) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(num)); } else { for (int i = index; i < num.size(); i++) { swap(num, i, index); backTrack(result, num, index + 1 ); swap(num, i, index); } } } public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> permute (int [] num) { Arrays.sort(num); ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>result = new ArrayList <ArrayList<Integer>>(); ArrayList<Integer>list = new ArrayList <Integer>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < num.length; i++) { list.add(num[i]); } backTrack(result, list, 0 ); return result; } }
更容易理解的版本,就是每轮都选一个没填过的数字填进去,一开始排好序就可以保证字典输入了,上面那个方法空间复杂度低点,但差不多
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public void backTrack (ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>result, int [] nums, ArrayList<Integer>temp, boolean [] isDistance, int index) { if (index == nums.length) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(temp)); return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (isDistance[i]) { continue ; } isDistance[i] = true ; temp.add(nums[i]); backTrack(result, nums, temp, isDistance, index + 1 ); isDistance[i] = false ; temp.remove(temp.size() - 1 ); } } public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> permute (int [] num) { Arrays.sort(num); ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>result = new ArrayList <ArrayList<Integer>>(); boolean [] isDistance = new boolean [num.length]; backTrack(result, num, new ArrayList <Integer>(), isDistance, 0 ); return result; } }
BM56 有重复项数字的全排列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public void backTrack (ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>result, int [] num, boolean [] isDistance, ArrayList<Integer>temp, int index) { if (index == num.length) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(temp)); return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < num.length; i++) { if (isDistance[i]) { continue ; } if (i > 0 && num[i] == num[i - 1 ] && !isDistance[i - 1 ]) { continue ; } isDistance[i] = true ; temp.add(num[i]); backTrack(result, num, isDistance, temp, index + 1 ); isDistance[i] = false ; temp.remove(temp.size() - 1 ); } } public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> permuteUnique (int [] num) { Arrays.sort(num); ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>result = new ArrayList <ArrayList<Integer>>(); backTrack(result, num, new boolean [num.length], new ArrayList <Integer>(), 0 ); return result; } }
BM57 岛屿数量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public void backTrack (char [][] grid, int i, int j) { grid[i][j] = '0' ; if (i > 0 && grid[i - 1 ][j] == '1' ) { backTrack(grid, i - 1 , j); } if (i + 1 < grid.length && grid[i + 1 ][j] == '1' ) { backTrack(grid, i + 1 , j); } if (j > 0 && grid[i][j - 1 ] == '1' ) { backTrack(grid, i, j - 1 ); } if (j + 1 < grid[0 ].length && grid[i][j + 1 ] == '1' ) { backTrack(grid, i, j + 1 ); } } public int solve (char [][] grid) { int result = 0 ; int m = grid.length; if (m == 0 ) { return result; } int n = grid[0 ].length; if (n == 0 ) { return result; } for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (grid[i][j] == '1' ) { result++; backTrack(grid, i, j); } } } return result; } }
BM58 字符串的排列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public void backTrack (ArrayList<String>result, String str, StringBuilder temp, boolean [] isDistance, int index) { if (index == str.length()) { result.add(new String (temp)); return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < str.length(); i++) { if (isDistance[i]) { continue ; } if (i > 0 && str.charAt(i - 1 ) == str.charAt(i) && !isDistance[i - 1 ]) { continue ; } temp.append(str.charAt(i)); isDistance[i] = true ; backTrack(result, str, temp, isDistance, index + 1 ); temp.deleteCharAt(temp.length() - 1 ); isDistance[i] = false ; } } public ArrayList<String> Permutation (String str) { ArrayList<String> result = new ArrayList <String>(); char [] chars = str.toCharArray(); Arrays.sort(chars); backTrack(result, new String (chars), new StringBuilder (), new boolean [str.length()], 0 ); return result; } }
BM60 括号生成
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public void backTrack (int left, int right, ArrayList<String>result, String temp, int n) { if (left == n && right == n) { result.add(temp); return ; } if (left < n) { backTrack(left + 1 , right, result, temp + "(" , n); } if (right < n && left > right) { backTrack(left, right + 1 , result, temp + ")" , n); } } public ArrayList<String> generateParenthesis (int n) { ArrayList<String>result = new ArrayList <String>(); backTrack(0 , 0 , result, "" , n); return result; } }
简单好理解,没有缓存
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 import java.util.*;public class Solution { int result = 0 ; public void backTrack (int i, int j, int [][] matrix, int last, int index) { if (i < 0 || i >= matrix.length || j < 0 || j >= matrix[0 ].length || matrix[i][j] <= last) { result = Math.max(result, index); return ; } backTrack(i - 1 , j, matrix, matrix[i][j], index + 1 ); backTrack(i + 1 , j, matrix, matrix[i][j], index + 1 ); backTrack(i, j - 1 , matrix, matrix[i][j], index + 1 ); backTrack(i, j + 1 , matrix, matrix[i][j], index + 1 ); } public int solve (int [][] matrix) { for (int i = 0 ; i < matrix.length; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < matrix[0 ].length; j++) { backTrack(i, j, matrix, -1 , 0 ); } } return result; } }
动态规划
BM62 斐波那契数列
递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int Fibonacci (int n) { if (n <= 2 ) { return 1 ; } return Fibonacci(n - 1 ) + Fibonacci(n - 2 ); } }
迭代
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int Fibonacci (int n) { if (n <= 2 ) { return 1 ; } int first = 1 , second = 1 ; for (int i = 2 ; i < n; i++) { int temp = first + second; first = second; second = temp; } return second; } }
BM63 跳台阶
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int jumpFloor (int number) { int first = 1 , second = 1 ; for (int i = 2 ; i <= number; i++) { int temp = first + second; first = second; second = temp; } return second; } }
BM64 最小花费爬楼梯
step 1:可以用一个数组记录每次爬到第i阶楼梯的最小花费,然后每增加一级台阶就转移一次状态,最终得到结果。
step 2:(初始状态) 因为可以直接从第0级或是第1级台阶开始,因此这两级的花费都直接为0.
step 3:(状态转移) 每次到一个台阶,只有两种情况,要么是它前一级台阶向上一步,要么是它前两级的台阶向上两步,因为在前面的台阶花费我们都得到了,因此每次更新最小值即可,转移方程为:dp[i]=min(dp[i−1]+cost[i−1],dp[i−2]+cost[i−2])。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int minCostClimbingStairs (int [] cost) { int [] dp = new int [cost.length + 1 ]; for (int i = 2 ; i <= cost.length; i++) { dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i - 1 ] + cost[i - 1 ], dp[i - 2 ] + cost[i - 2 ]); } return dp[cost.length]; } }
<a name=””
字符串
BM83 字符串变形
用内置函数的reverse()翻转也可以
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public String trans (String s, int n) { char [] result = new char [n]; int count = 0 ; for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { int j = i; while (j >= 0 && s.charAt(j) != ' ' ) { j--; } String temp = s.substring(j + 1 , i + 1 ); for (int k = 0 ; k < temp.length(); k++) { char c = temp.charAt(k); if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z' ) { c = ((char )(c - 'A' + 'a' )); } else { c = ((char )(c + 'A' - 'a' )); } result[count++] = c; } if (count < result.length) { result[count++] = ' ' ; } i = j; } return new String (result); } }
BM84 最长公共前缀
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public String longestCommonPrefix (String[] strs) { if (strs.length == 0 ) { return "" ; } int largest = 0 , target = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < strs.length; i++) { if (strs[i].length() > largest) { largest = strs[i].length(); target = i; } } int index = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < largest; i++) { char c = strs[target].charAt(i); for (int j = 0 ; j < strs.length; j++) { if ((strs[j].length() > i && strs[j].charAt(i) == c) || j == target) { continue ; } return strs[target].substring(0 , i); } } return strs[target].substring(0 , strs[target].length()); } }
BM85 验证IP地址
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ``` <a id="BM86 大数加法" ></a> **BM86 大数加法** ```java
双指针
BM88 判断是否为回文字符串
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public boolean judge (String str) { int left = 0 , right = str.length() - 1 ; while (left < right) { if (str.charAt(left++) != str.charAt(right--)) { return false ; } } return true ; } }
BM89 合并区间
跟主持人调度很像,排序+贪心,下面是个人想法
其实就是找交叉区间
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public ArrayList<Interval> merge (ArrayList<Interval> intervals) { ArrayList<Interval> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (!intervals.isEmpty()) { int [] start = new int [intervals.size()]; int [] end = new int [intervals.size()]; for (int i = 0 ; i < intervals.size(); i++) { start[i] = intervals.get(i).start; end[i] = intervals.get(i).end; } Arrays.sort(start, 0 , start.length); Arrays.sort(end, 0 , end.length); int left_value = start[0 ], right_value = end[0 ]; for (int left = 1 , right = 1 ; left < start.length; left++, right++) { if (start[left] > right_value) { result.add(new Interval (left_value, right_value)); left_value = start[left]; right_value = end[right]; } else { if (end[right] > right_value) { right_value = end[right]; } } } result.add(new Interval (left_value, right_value)); } return result; } }
BM91 反转字符串
直接复制一个数组然后逆序放到新数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public String solve (String str) { char [] result = str.toCharArray(); int len = str.length(); for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++) { result[len - 1 - i] = str.charAt(i); } return new String (result); } }
减少操作时间
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public String solve (String str) { char [] result = str.toCharArray(); int len = str.length(); for (int i = 0 ;i<len/2 ;i++){ char temp = str.charAt(i); result[i] = result[len-1 -i]; result[len-1 -i] = temp; } return new String (result); } }
BM92 最长无重复子数组
我们使用两个指针,一个i一个j,最开始的时候i和j指向第一个元素,然后i往后移,把扫描过的元素都放到map中,如果i扫描过的元素没有重复的就一直往后移,顺便记录一下最大值max,如果i扫描过的元素有重复的,就改变j的位置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int maxLength (int [] arr) { int max = 0 ; Set<Integer>set = new HashSet <>(); int left = 0 , right = 0 ; while (right < arr.length) { if (set.contains(arr[right])) { set.remove(arr[left++]); } else { set.add(arr[right++]); max = Math.max(max, set.size()); } } return max; } }
BM93 盛水最多的容器
双指针指的是在遍历对象的过程中,不是普通的使用单个指针进行访问,而是使用两个指针(特殊情况甚至可以多个),两个指针或是同方向访问两个链表、或是同方向访问一个链表(快慢指针)、或是相反方向扫描(对撞指针),从而达到我们需要的目的。
这里还有贪心思想,贪心策略是每次移动的指针是移动指针指向的高度较短的那个
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int maxArea (int [] height) { int max = 0 ; if (height.length < 2 ) { return 0 ; } int left = 0 , right = height.length - 1 ; while (left < right) { if ((right - left) * Math.min(height[right], height[left]) > max) { max = (right - left) * Math.min(height[right], height[left]) ; } if (height[right] > height[left]) { left++; } else { right--; } } return max; } }
贪心算法
BM96 主持人调度(二)
贪心思想属于动态规划思想中的一种,其基本原理是找出整体当中给的每个局部子结构的最优解,并且最终将所有的这些局部最优解结合起来形成整体上的一个最优解。
我们利用贪心思想,什么时候需要的主持人最少?那肯定是所有的区间没有重叠,每个区间首和上一个的区间尾都没有相交的情况,我们就可以让同一位主持人不辞辛劳,一直主持了。但是题目肯定不是这种理想的情况,那我们需要对交叉部分,判断需要增加多少位主持人 。
step 1: 利用辅助数组获取单独各个活动开始的时间和结束时间,然后分别开始时间和结束时间进行排序,方便后面判断是否相交。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int minmumNumberOfHost (int n, int [][] startEnd) { int need_people = 0 ; int [] start = new int [n]; int [] end = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { start[i] = startEnd[i][0 ]; end[i] = startEnd[i][1 ]; } Arrays.sort(start, 0 , start.length); Arrays.sort(end, 0 , end.length); int j = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (start[i] >= end[j]) { j++; } else { need_people++; } } return need_people; } }
模拟
BM97旋转数组
方法一:使用额外数组,然后遍历每个数字放到正确位置后返回数组
方法二:三次翻转(推荐使用)
循环右移相当于从第m个位置开始,左右两部分视作整体翻转。即abcdefg右移3位efgabcd可以看成AB翻转成BA(这里小写字母看成数组元素,大写字母看成整体)。既然是翻转我们就可以用到reverse函数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int [] solve (int n, int m, int [] a) { m = m % n; reverse(a, 0 , n - 1 ); reverse(a, 0 , m - 1 ); reverse(a, m, n - 1 ); return a; } public void reverse (int [] a, int start, int end) { while (start < end) { int temp = a[start]; a[start] = a[end]; a[end] = temp; start++; end--; } } }
BM99 顺时针旋转矩阵
方法一:直接复制一个二维数组填入返回即可,第i行换到第n-i列(关系是初始位置的横坐标+换后的纵坐标=n),换之前的纵坐标和换之后的横坐标相等
方法二:沿右下对角线翻转,再左右翻转;也可以沿左上对角线翻转,再上下翻转
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public int [][] rotateMatrix (int [][] mat, int n) { if (n!=0 ){ diagonalReverse(mat,n); leftRightReverse(mat,n); } return mat; } public void upDownReverse (int [][]mat,int n) { for (int i = 0 ;i<n/2 ;i++){ for (int j = 0 ;j<n;j++){ int temp = mat[i][j]; mat[i][j] = mat[n-1 -i][j]; mat[n-1 -i][j] = temp; } } } public void leftRightReverse (int [][]mat,int n) { for (int i = 0 ;i<n;i++){ for (int j = 0 ;j<n/2 ;j++){ int temp = mat[i][j]; mat[i][j] = mat[i][n-1 -j]; mat[i][n-1 -j] = temp; } } } public void diagonalReverse (int [][]mat,int n) { for (int i = 0 ;i<n;i++){ for (int j = i+1 ;j<n;j++){ int temp = mat[i][j]; mat[i][j] = mat[j][i]; mat[j][i] = temp; } } } }
BM100 设计LRU缓存结构
BM101 设计LFU缓存结构